Lesogaberan
Lesogaberan
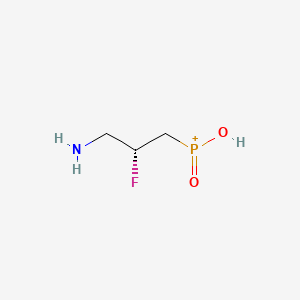
AZD-3355, AZD3355, [(2R)-3-amino-2-fluoropropyl]phosphinic acid, 344413-67-8
Molecular Formula: C3H8FNO2P+
Molecular Weight: 140.073285 g/mol
[(2R)-3-amino-2-fluoropropyl]-hydroxy-oxophosphanium
Lesogaberan (AZD-3355) was[1] an experimental drug candidate developed byAstraZeneca for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).[2] As a GABABreceptor agonist,[3] it has the same mechanism of action as baclofen, but is anticipated to have fewer of the central nervous system side effects that limit the clinical use of baclofen for the treatment of GERD.[4]
J. Med. Chem., 2008, 51 (14), pp 4315–4320
DOI: 10.1021/jm701425k
We have previously demonstrated that the prototypical GABAB receptor agonist baclofen inhibits transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations (TLESRs), the most important mechanism for gastroesophageal reflux. Thus, GABAB agonists could be exploited for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. However, baclofen, which is used as an antispastic agent, and other previously known GABAB agonists can produce CNS side effects such as sedation, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting at higher doses. We now report the discovery of atypical GABAB agonists devoid of classical GABAB agonist related CNS side effects at therapeutic doses and the optimization of this type of compound for inhibition of TLESRs, which has resulted in a candidate drug (R)-7 (AZD3355) that is presently being evaluated in man.
(2R)-(3-Amino-2-fluoropropyl)phosphinic Acid ((R)-7)
(R)-7 as a white solid (3.12 g, 24%):
mp = 183−185 °C;
1H NMR (300 MHz, D2O) δ 7.90 (s, 0.5 H), 6.15 (s, 0.5 H), 5.12−5.29 (m, 0.5 H), 4.92−5.10 (m, 0.5 H), 3.12−3.42 (m, 2H), 1.74−2.26 (m, 2H);
[α]D25 −4.0° (c 1.0, H2O);
APIMS m/z 142 [M + H]+. Anal. (C3H9FNO2P·0.25H2O) C, H, N.
References
- AstraZeneca. “AZD3355″. Retrieved 30 December 2011.
- Bredenoord, Albert J. (2009). “Lesogaberan, a GABAB agonist for the potential treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease”. IDrugs 12 (9): 576–584.PMID 19697277.
- Alstermark, et al.; Amin, K; Dinn, SR; Elebring, T; Fjellström, O; Fitzpatrick, K; Geiss, WB; Gottfries, J et al. (2008). “Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type B (GABAB) Receptor Agonists as Gastroesophageal Reflux Inhibitors”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 51 (14): 4315–4320.doi:10.1021/jm701425k. PMID 18578471.
- Brian E. Lacy, Robert Chehade, and Michael D. Crowell (2010). “Lesogaberan”.Drugs of the Future 35 (12): 987–992. doi:10.1358/dof.2010.035.012.1540661.
| LESOGABERAN | |
|---|---|
| IDENTIFIERS | |
| CAS number | 344413-67-8 |
| PubChem | 9833984 |
| ChemSpider | 23254384 |
| UNII | 4D6Q6HGC7Z |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL448343 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| PROPERTIES | |
| Molecular formula | C3H9FNO2P |
| Molar mass | 141.08 g mol−1 |
No comments:
Post a Comment