1 PAMICOGREL
2.
3.
4.


1 PAMICOGREL


 pamicogrel
pamicogrel
 pamicogrel
pamicogrel


2.
3.
4.


1 PAMICOGREL

Pamicogrel
CAS 101001-34-7
D01090, TO-192, KBT-3022, KB-3022, Paminate, UNII-398FD8EDAL
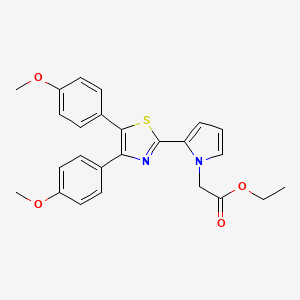
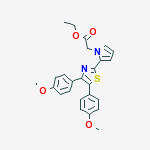
2-[4,5-Bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-thiazolyl]-1H-pyrrole-1-acetic acid ethyl ester
Ethyl 2-[4,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)thiazol-2-yl]-pyrrole-1-acetate
ethyl 2-[4,5-bis(p-methoxyphenyl)-2-thiazolyl]pyrrole-1-acetate
Manufacturers' Codes: KB-3022; KBT-3022
Antiplatelet Therapy, Coagulation Disorders Therapy, HEMATOLOGIC DRUGS, Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
Molecular Formula: C25H24N2O4S
Molecular Weight: 448.53
Percent Composition: C 66.94%, H 5.39%, N 6.25%, O 14.27%, S 7.15%
Properties: Crystals from ligroin, mp 132.5-135.5°.
Melting point: mp 132.5-135.5°
Toxicity data: LD50 orally in male mice: >3000 mg/kg (Yoshino)
Therap-Cat: Antithrombotic.
. PAMICOGREL
PAMICOGREL
 PAMICOGREL
PAMICOGREL
Pamicogrel (CAS NO.: 101001-34-7), with its systematic name of 1H-Pyrrole-1-acetic acid, 2-(4,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-thiazolyl)-, ethyl ester, could be produced through many synthetic methods.
Following is one of the synthesis routes:
alpha-Bromo-4,4-dimethoxidesoxybenzoin (I) is cyclized with pyrrole-2-carbothioamide (II) in hot acetonitrile to produce 4,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(pyrrol-2-yl)thiazole (III), which is then condensed with ethyl bromoacetate (IV) in the prsence of NaOH and tetrabutylammonium bromide in refluxing dichloromethane - water.
alpha-Bromo-4,4-dimethoxidesoxybenzoin (I) is cyclized with pyrrole-2-carbothioamide (II) in hot acetonitrile to produce 4,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(pyrrol-2-yl)thiazole (III), which is then condensed with ethyl bromoacetate (IV) in the prsence of NaOH and tetrabutylammonium bromide in refluxing dichloromethane - water.

The cyclization of alpha-bromo-4,4'-dimethoxydesoxybenzoin (I) with pyrrole-2-carbothioamide (II) in hot acetonitrile gives 4,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(pyrrol-2-yl)thiazole (III), which is then condensed with ethyl bromoacetate (IV) by means of NaOH and tetrabutylammonium bromide in refluxing dichloromethane - water
EP 0159677; JP 1985222481; JP 1986033186; JP 1986200985; US 4659726
SYNTHESIS
- Reaction Scheme-I:
-
wherein R is as defined above, and Y is a halogen such as chlorine, bromine or iodine, or p-toluenesulfonyloxy group.
- The process of the above reaction scheme-I can be carried out by reacting a compound (II) and an equimolar or excess amount of a compound (III) in the presence of a base or a phase transfer catalyst. In case of using a base such as metallic potassium, metallic sodium, potassium tert-butoxide etc.; the reaction is carried out in a solvent of tetrahydrofuran or dimethoxyethane at a temperature of from room temperature to a boiling point of the solvent for 1 to 24 hours. In case of using a phase transfer catalyst such as a quaternary ammonium salt (e.g. tetra-n-butylammonium bromide, methyltrioctylammonium chloride, etc.), the reaction is carried out in two phases of benzene or dichloromethane and 50 % aqueous sodium hydroxide or 60 % aqeuous potassium hydroxide at a temperature of from 0°C to a boiling point of the solvent for one minute to 24 hours.
- Reaction Scheme-II:
-
wherein X is a halogen such as bromine or chlorine.
- The above process can be carried out by reacting a compound (IV) and an equimolar amount of a compound (V) in a solvent such as acetonitrile, dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), or an alcohol (e.g. ethanol) at a temperature of from 50°C to a boling point of the solvent for 10 minutes to 4 hours.
- Reaction Scheme-IV:
-
wherein R1 is as defined above.
- The process can be carried out by converting a compound (VII) into an oxime (VIII) by a conventional oxime forming reaction, heating the oxime (VIII) in acetic anhydride to obtain a compound (IX), and treating the compound (IX) with hydrogen sulfide, that is, by blowing hydrogen sulfide gas into a reaction system containing the compound (IX) in a solvent such as DMF, DMSO or pyridine in the presence of 0.5 to 5 equimolar amount of a base such as a tertiary amine (e.g. triethylamine) at a temperature of from 0° to 40°C for 3 to 24 hours
- Reference Example 6
- 4,5-Bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(pyrrol-2-yl)thiazole [compound of the formula (II)]:
- Pyrrole-2-carbothioamide (cf. J. Org. Chem., 38, 667, 1973) (1.51 g, 12 mmole) and α-bromo-4,4'-dimethoxy- deoxybenzoin (cf. Aust. J. Chem., 8, 385. 1955) (4.02 g, 12 mmole) are dissolved in acetonitrile (120 ml). The mixture is stirred at 60°C for 50 minutes. After the reaction, the reaction mixture is distilled under reduced pressure to remove the solvent. To the resulting residue are added chloroform and aqueous solution of sodium carbonate, and the mixture is shaken. The chloroform layer is taken, and the aqueous layer is further extracted with chloroform. The chloroform layers are combined, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and distilled under reduced pressure to remove the solvent. The residue is recrystallized from ligroin to give 4,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(pyrrol-2-yl)-thiazole (3.74 g, yield: 86 %).
- M.p. 131.5 - 134.0°C
- NMR (CDCl3, δ ppm): 3.7 (6H) , 6.1 (1H, dd) , 6.5-6.9 (6H), 7.1-7.5 (4H), 9.4-9.8 (lH).
- Elementary analysis for C21H18N2O2S:
- Example 14
- Ethyl 2-[4,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)thiazol-2-yl]-pyrrole-1-acetate (compound of the formula (I) wherein R1 = -CH2-COOC2H5):
- 4,5-Bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(pyrrol-2-yl)thiazole obtained in the same manner as described in Reference Example 6 (3.62 g, 10 mmole), ethyl bromoacetate (1.67 g, 10 mmole), and tetra-n-butylammonium bromide (0.32 g, 1 mmole) are refluxed with vigorous stirring in two phases of dichloromethane (40 ml) and 50 % aqueous sodium hydroxide (40 ml) at room temperature for 2 minutes. To the mixture are added water and dichloromethane under ice-cooling, and the mixture is shaken. The dichloromethane layer is taken, and the aqueous layer is further extracted with dichloromethane. The dichloromethane layers are combined, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and distilled under reduced pressure to remove the solvent. The residue is recrystallized from ligroin to give ethyl 2-[4,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)thiazol-2-yl]pyrrole-1-acetate (3.64 g, yield: 81 %).
- M.p. 132.5 - 135.5°C
- NMR (CDCl3, δ ppm): 1.2 (3H, t), 3.8 (6H), 4.15 (2H, q), 5.25 (2H, s), 6.25 (1H, dd), 6.7-6.95 (6H), 7.2-7.55 (4H).
- Elementary analysis for C25H24N2O4S:
Literature References:
Cyclooxygenase inhibitor. Prepn: K. Yoshino et al., EP 159677; eidem, US 4659726 (1985, 1987 both to Kanebo).
Drugs Fut1991,16,(2):105
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1992 , vol. 40, 11 pg. 3048 - 3051
HPLC determn in plasma and urine: Y. Nakada et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull. 38, 1093 (1990).
Pharmacokinetics: Y. Nakada et al., Yakuzaigaku 53, 210 (1993), C.A. 120, 315100 (1993).
Activity as antithrombotic: K. Yokoto et al., Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 68, 201 (1995); as platelet aggregation inhibitor: K. Yokoto et al., J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47, 768 (1995).
Evaluation of cerebral protective effects: N. Yamamoto et al., Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 69, 421 (1995); eidem, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 297, 225 (1996).
Determination of the antiplatelet agent. KB-3022, and its metabolite by high-performance liquid chromatography.Nakada Y, Ikuta Y, Kawashima T, Awata N.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1990 Apr;38(4):1093-5.
 pamicogrel
pamicogrel
PATENTS
| EP0037274A1 * | 30 Mar 1981 | 7 Oct 1981 | Eli Lilly And Company | Substituted triaryl thiazole compounds |
| EP0077024A2 * | 7 Oct 1982 | 20 Apr 1983 | Schering Aktiengesellschaft | Imidazole derivatives, process for their preparation and pharmaceutical products containing them |
| US4168315 * | 28 Sep 1977 | 18 Sep 1979 | The Upjohn Company | Dianisyl thiazole compound, compositions and method of antithrombotic treatment |


.......
2.










Aten 50mg Tablet is belongs to the group of medicines known as beta-blockers, which are used to treat blood pressure and heart strain. take the full dose of medicine as per the doctor's guidance. you can take this tablet with or without food.
ReplyDelete