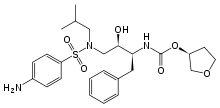
AMPRENAVIR
Amprenavir (Agenerase, GlaxoSmithKline) is a protease inhibitor used to treat HIV infection. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on April 15, 1999, for twice-a-day dosing instead of needing to be taken every eight hours. The convenient dosing came at a price, as the dose required is 1,200 mg, delivered in eight very large gel capsules.
Production of amprenavir was discontinued by the manufacturer December 31, 2004; a prodrug version (fosamprenavir) is available.
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| (3S)-oxolan-3-yl N-[(2S,3R)-3-hydroxy-4-[N-(2-methylpropyl)(4-aminobenzene)sulfonamido]-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Agenerase |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a699051 |
| Licence data | EMA:Link, US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy cat. | C (US) |
| Routes | oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Half-life | 7.1-10.6 hours |
| Excretion | <3% renal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 161814-49-9 |
| ATC code | J05AE05 |
| PubChem | CID 65016 |
| DrugBank | DB00701 |
| ChemSpider | 58532 |
| UNII | 5S0W860XNR |
| KEGG | D00894 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:40050 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL116 |
| NIAID ChemDB | 006080 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C25H35N3O6S |
| Mol. mass | 505.628 g/mol |
Amprenavir (Agenerase, GlaxoSmithKline) is a protease inhibitor used to treat HIV infection. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on April 15, 1999, for twice-a-day dosing instead of needing to be taken every eight hours. The convenient dosing came at a price, as the dose required is 1,200 mg, delivered in eight very large gel capsules.
Production of amprenavir was discontinued by the manufacturer December 31, 2004; a prodrug version (fosamprenavir) is available
......................
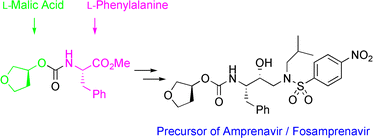
New approaches to the industrial synthesis of HIV protease inhibitors
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2004/ob/b404071f/unauth#!divAbstract
Efficient and industrially applicable synthetic processes for precursors of HIV protease inhibitors (Amprenavir, Fosamprenavir) are described. These involve a novel and economical method for the preparation of a key intermediate, (3S)-hydroxytetrahydrofuran, from L-malic acid. Three new approaches to the assembly of Amprenavir are also discussed. Of these, a synthetic route in which an (S)-tetrahydrofuranyloxy carbonyl is attached to L-phenylalanine appears to be the most promising manufacturing process, in that it offers satisfactory stereoselectivity in fewer steps.
...........................................................................
 |
Amprenavir is a white to cream-colored solid with a solubility of approximately 0.04 mg/mL in water at 25°C.
AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) are
available for oral administration. Each 50- mg capsule contains the inactive ingredients d-alpha tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS), polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400) 246.7 mg, and propylene glycol 19 mg. The capsule shell contains the inactive ingredients d-sorbitol and sorbitans solution, gelatin, glycerin, and titanium dioxide. The soft gelatin capsules are printed with edible red ink. Each 50- mg AGENERASE Capsule contains 36.3 IU vitamin E in the form of TPGS. The total amount of vitamin E in the recommended daily adult dose of AGENERASE is 1,744 IU.
See also
- Fosamprenavir, a prodrug of amprenavir
External links
- Amprenavir bound to proteins in the PDB
No comments:
Post a Comment